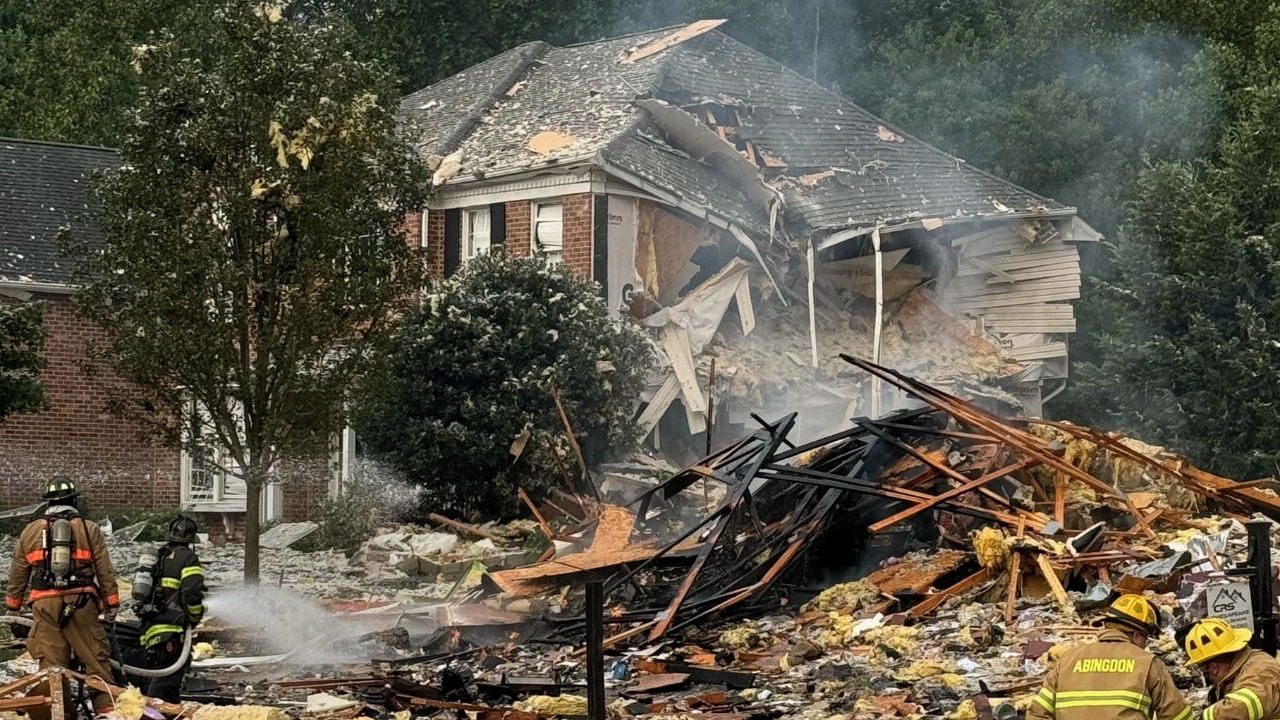
On its face, the case argued before the Supreme Court on Wednesday was about whether doctors in Idaho have the obligation to provide abortions to women facing emergency risks to their lives.
But a difference in word choice by the justices and the lawyers revealed a more fundamental debate, one that goes straight to the ultimate goal of the anti-abortion movement.
The lawyer for Idaho and the conservative justices including Samuel A. Alito Jr., who wrote the majority opinion overturning Roe v. Wade, employed the term “unborn child,” a term used in the federal law at issue. The lawyer for the Biden administration tended to say “fetus.”
It was not merely a matter of semantics: Anti-abortion groups argue that life begins at conception. They have long pushed to establish so-called fetal personhood laws, granting fetuses the same legal rights and protections as any person, in the hopes that it would establish that abortion at any point in pregnancy is murder.
Roe v. Wade stood in their way for five decades, prohibiting states from banning abortion before fetal viability, or roughly 24 weeks. But since the Supreme Court overturned that decision in June 2022, laws establishing fetal personhood have taken effect in Georgia and other states. And anti-abortion lawmakers in Congress and in state legislatures have pushed other measures that establish fetal personhood through a variety of means: giving tax credits for fetuses, for example, or requiring child support payments beginning at conception.
Legal scholars warn that laws establishing fetal personhood would go farther than even existing abortion bans, ruling out all or most of the exceptions that those bans allow. If life begins at conception, that would include pregnancies that result from incest or rape.
Abortion rights groups and the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists use “embryo” when talking about pregnancies up to eight weeks after the start of a woman’s last menstrual period, and “fetus” to describe anything between that and delivery. (ACOG guidelines say: “Centering the language on a future state of a pregnancy is medically inaccurate.”)
Justice Alito relied on the language of fetal personhood in writing the decision overturning Roe, citing several 19th-century state laws referring to “unborn children.”
On Wednesday, he pressed the solicitor general repeatedly on the question of the “unborn child.” He noted that the federal law regulating emergency care — the law at issue in the Idaho case — uses the phrase several times. That, he said, suggests that the federal law means that “the hospital must try to eliminate any immediate threat to the child, but performing an abortion is antithetical to that duty.”
Elizabeth Prelogar, the solicitor general, replied that the law used that phrase to refer to cases in which the health of the pregnancy was in danger; the Idaho case concerns emergency health risks to the mother. The lawyer for Idaho, however, argued that doctors have to consider the life of the “unborn child” as much as the rights of the pregnant woman, even when she is facing an emergency risk to her health.
Anti-abortion lawmakers and groups have said that fetal personhood laws are the first step toward their ultimate goal of establishing constitutional protection for life beginning at conception.
But even many voters who oppose abortion in whole or in part have rejected attempts to establish fetal personhood. Voters rejected initiatives twice in South Dakota, in 2006 and 2008, and in Mississippi in 2011. Doctors in those states warned that establishing fetal personhood would criminalize IUDs and other methods of birth control. They also warned that they would have to stop doing in vitro fertilization, because disposing of unused fertilized eggs, or selectively eliminating implanted eggs, as many aspiring parents do, could result in murder charges.